Global Power Battery Recycling Market Poised for Strategic Growth as First Major Retirement Wave Hits
Date : 2026-02-04
Reading : 207
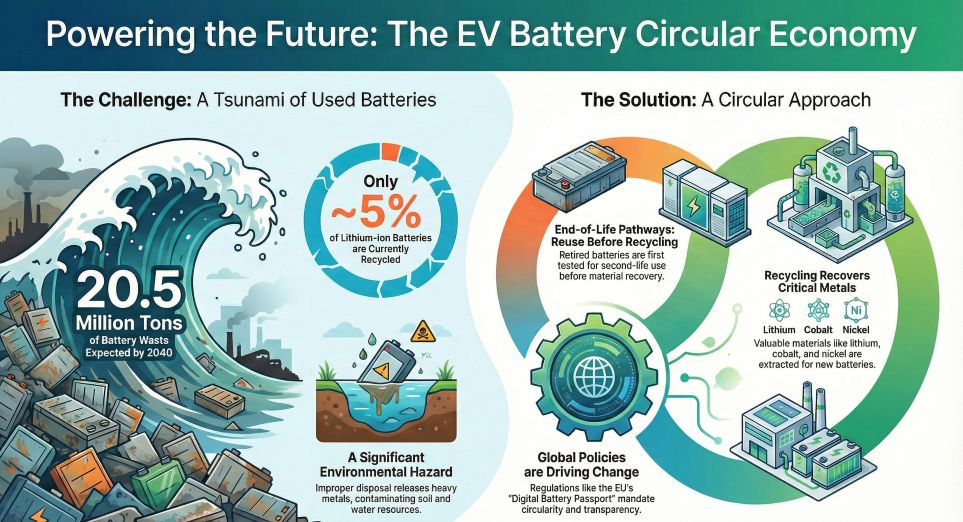
The global power battery recycling industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation, transitioning from a fragmented waste management sector into a sophisticated strategic resource hub. According to market analysis, the first massive wave of electric vehicle (EV) battery retirements is starting in the 2024-2026 period, following the rapid adoption of EVs between 2015 and 2018. By 2030, battery retirement volumes in China alone are expected to exceed 1 million tons, with some aggressive forecasts reaching 3.5 million tons.
Figure Powering the Future: The EV Battery Circular Economy
 Regulatory Revolution: Vehicle-Battery Integration and Digital IDs
Regulatory Revolution: Vehicle-Battery Integration and Digital IDs
A new regulatory era is set to begin on April 1, 2026, with the implementation of the Management Measures for the Recycling and Utilization of Waste Power Batteries for New Energy Vehicles in China. Two core mechanisms are expected to eliminate illegal small-scale workshops and stabilize the supply chain for authorized recyclers.
First, the vehicle-battery integration system mandates that vehicles and batteries remain bundled during the scrapping process. This prevents the previous practice where batteries were stripped and sold to unregulated channels before the vehicle reached certified dismantling plants. Second, the digital battery passport (Digital ID) will provide a dynamic, traceable record of a battery’s entire life cycle, from production to recycling. This technology aligns with the EU New Battery Law, ensuring global compliance and transparency in material sourcing.
Profitability Dynamics: The Lithium Price Influence
The economic viability of recycling, particularly for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries, is highly sensitive to lithium carbonate prices. Unlike ternary batteries which contain high-value nickel and cobalt, LFP recycling profitability is almost entirely dependent on lithium recovery.
Market data suggests a critical breakeven point for LFP recycling. When lithium carbonate prices fall below 60,000 RMB per ton, LFP recycling often results in a net loss. The survival line for most authorized recyclers is approximately 100,000 RMB per ton. However, analysts predict that as lithium prices stabilize and potentially return to the 180,000 RMB per ton range by 2026, LFP recycling will enter a high-profit era. Leading firms like CATL (Brunp) and GEM have already achieved lithium recovery rates exceeding 95%, significantly lowering the breakeven threshold.
Technological Evolution and Geopolitical Challenges
Hydrometallurgy remains the dominant global technology due to its high recovery rates for nickel and cobalt (98%+) and lithium (90%+). However, direct recycling is emerging as a high-potential alternative, promising up to 50% cost savings and an 80% reduction in carbon footprint by repairing the cathode structure without complete chemical breakdown.
Geopolitically, the industry faces the EU's ban on the export of black mass—the intermediate powder from crushed batteries—to non-OECD countries. This policy forces a shift from a resource-return model to a localized capacity model. Chinese recycling giants are now accelerating the construction of full-scale hydrometallurgical facilities within the EU to comply with recycled content mandates set for 2031, which require new batteries to contain specific percentages of recycled cobalt, lithium, and nickel.
Table Global Power Battery Recycling Leaders and Capacity Analysis
Future Outlook: 2026-2030
The period between 2026 and 2030 will mark the maturation of the global battery recycling value chain. As logistics costs—currently accounting for nearly 50% of total costs due to dangerous goods classification—are optimized through regionalized hubs, and as the vehicle-battery integration system secures feedstock for authorized white-list enterprises, the industry will move past its current phase of underutilization. Enterprises that master high-efficiency lithium extraction and secure localized international capacity will be the primary beneficiaries of this 100-billion-dollar resource cycle.
HDIN Research
Company Profile: HDIN Research focuses on providing market consulting services. As an independent third-party consulting firm, it is committed to providing in-depth market research and analysis reports.
Official Website: www.hdinresearch.com
Contact Email: sales@hdinresearch.com
Figure Powering the Future: The EV Battery Circular Economy
 Regulatory Revolution: Vehicle-Battery Integration and Digital IDs
Regulatory Revolution: Vehicle-Battery Integration and Digital IDsA new regulatory era is set to begin on April 1, 2026, with the implementation of the Management Measures for the Recycling and Utilization of Waste Power Batteries for New Energy Vehicles in China. Two core mechanisms are expected to eliminate illegal small-scale workshops and stabilize the supply chain for authorized recyclers.
First, the vehicle-battery integration system mandates that vehicles and batteries remain bundled during the scrapping process. This prevents the previous practice where batteries were stripped and sold to unregulated channels before the vehicle reached certified dismantling plants. Second, the digital battery passport (Digital ID) will provide a dynamic, traceable record of a battery’s entire life cycle, from production to recycling. This technology aligns with the EU New Battery Law, ensuring global compliance and transparency in material sourcing.
Profitability Dynamics: The Lithium Price Influence
The economic viability of recycling, particularly for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries, is highly sensitive to lithium carbonate prices. Unlike ternary batteries which contain high-value nickel and cobalt, LFP recycling profitability is almost entirely dependent on lithium recovery.
Market data suggests a critical breakeven point for LFP recycling. When lithium carbonate prices fall below 60,000 RMB per ton, LFP recycling often results in a net loss. The survival line for most authorized recyclers is approximately 100,000 RMB per ton. However, analysts predict that as lithium prices stabilize and potentially return to the 180,000 RMB per ton range by 2026, LFP recycling will enter a high-profit era. Leading firms like CATL (Brunp) and GEM have already achieved lithium recovery rates exceeding 95%, significantly lowering the breakeven threshold.
Technological Evolution and Geopolitical Challenges
Hydrometallurgy remains the dominant global technology due to its high recovery rates for nickel and cobalt (98%+) and lithium (90%+). However, direct recycling is emerging as a high-potential alternative, promising up to 50% cost savings and an 80% reduction in carbon footprint by repairing the cathode structure without complete chemical breakdown.
Geopolitically, the industry faces the EU's ban on the export of black mass—the intermediate powder from crushed batteries—to non-OECD countries. This policy forces a shift from a resource-return model to a localized capacity model. Chinese recycling giants are now accelerating the construction of full-scale hydrometallurgical facilities within the EU to comply with recycled content mandates set for 2031, which require new batteries to contain specific percentages of recycled cobalt, lithium, and nickel.
Table Global Power Battery Recycling Leaders and Capacity Analysis
| Company Name | Annual Recycling Capacity | Key Recovery Rates | Strategic Partnerships & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL (Brunp) | 270,000 tons | Li: 93.8% Ni/Co/Mn: 99.6% | Closed-loop agreements with Volvo and Mercedes-Benz |
| GEM | 550,000 tons | Li: 95%+ Ni/Co: 99%+ | Target of 500,000 tons by 2030; Indonesian talent cooperation |
| SK On | ≈30 GWh | High efficiency Lithium Hydroxide | Joint venture with SungEel; black mass contracts with Ecopro |
| LG Energy Solution | ≈80 GWh (Global Layout) | High automation and refining | North American localization with Li-Cycle |
| Samsung SDI | ≈50 GWh | — | Target 30% utilization by 2025; Stakeholder in SungEel HiTech; JV with General Motors |
Future Outlook: 2026-2030
The period between 2026 and 2030 will mark the maturation of the global battery recycling value chain. As logistics costs—currently accounting for nearly 50% of total costs due to dangerous goods classification—are optimized through regionalized hubs, and as the vehicle-battery integration system secures feedstock for authorized white-list enterprises, the industry will move past its current phase of underutilization. Enterprises that master high-efficiency lithium extraction and secure localized international capacity will be the primary beneficiaries of this 100-billion-dollar resource cycle.
HDIN Research
Company Profile: HDIN Research focuses on providing market consulting services. As an independent third-party consulting firm, it is committed to providing in-depth market research and analysis reports.
Official Website: www.hdinresearch.com
Contact Email: sales@hdinresearch.com